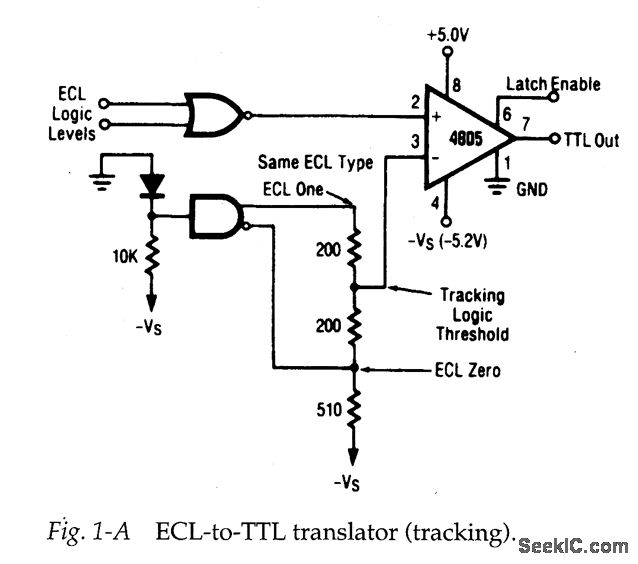
Electrical Engineering Stack Exchange Circuit Diagram Design Example: Level-to-Pulse • A level-to-pulse converter produces a single-cycle pulse each time its input goes high. • It's a synchronous rising-edge detector. • Sample uses: - Buttons and switches pressed by humans for arbitrary periods of time - Single-cycle enable signals for counters Level to Pulse Converter L P CLK Whenever

What I found were forums packed with very intelligent people working on homebrew detectors, schematics, circuits, and designs with the electrical engineering knowledge to make very interesting and cost effective metal detectors. I was delighted to find several schematics for Pulse Induction, VLF, and CCO detectors on the Geotech forum. Otherwise, the output pulse width will be same as the input pulse width. That is without Q3 transistor, the output pulse follows the input pulse. The R and C values used are 47KOhm and 47uF each which gives a pulse width of 2.2 seconds. You can use the online RC time constant calculator to find out the R and C values for give time period. The
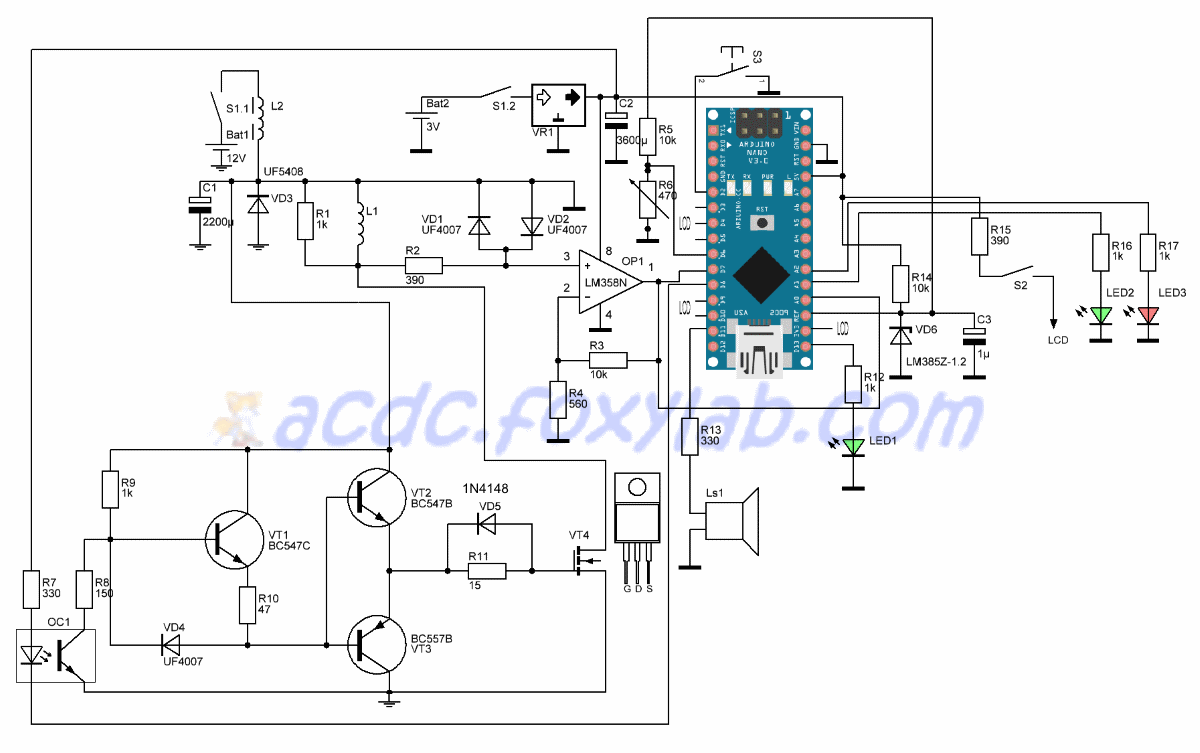
How to build a Surf PI 1.2 pulse induction metal detector from a DIY ... Circuit Diagram
The deep penetration and wide coverage area of pulse induction detectors also make them ideal for searching in large open spaces, such as fields or parks, where targets can be spread out over a wide area. Step 3: Assembling the Circuit. pulse induction metal detector, circuit, assembling, step-by-step guide, building, components, connection

This application note describes how to create a programmable push-button, pulse detector, and pulse generator using the voltage supervisor family: TPS3895, TPS3896, TPS3897, and TPS3898. This
Arduino Based Pulse Induction Detector Circuit Diagram
This circuit may be converted into a negative-edge pulse detector circuit with only a change of the final gate from AND to NOR: Now that we know how a pulse detector can be made, we can show it attached to the enable input of a latch to turn it into a flip-flop. In this case, the circuit is a S-R flip-flop: Using this circuit you will having a working PI detector with only 8-10 external components (depending if the OLED display and/or a speaker is used). Step 4: Setting Up and Using the Detector If the detector is build properly and the program is written to the Arduino, the easiest (if not the only) way of setting the unit up is to use an OLED One solution would be to add more inverters to your pulse generator. Another would be to use a differential detector with a lower threshold and higher input impedence. You need to create a specification for your circuit. E.g., what are the static timing characteristics of the pulse you want to detect?